Aptima® CMV Quant Assay
Confident Cytomegalovirus (CMV) testing results for viral load testing in plasma and whole blood.
Information for Healthcare Professionals
Overview
Documents
Accurate & Highly Reproducible Quantification
An assay that quantifies the viral load of CMV during the management of solid-organ transplant and haematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. This in vitro nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) uses real-time transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) technology on the fully automated Panther® System with human plasma and whole blood samples.1
Sample-To-Result within a Single Integrated Instrument
Enhancing patient management following transplant surgery with the preferred method of monitoring CMV infection2 matters. The Aptima CMV Quant assay on the Panther System combines assay performance and excellent automation for viral load monitoring.
Rapid Turnaround Time & Random Access
No more batching, simply load samples with different test orders as they arrive. STAT result option is available with the ability to prioritise results. You can attain the first results in about 3 hours.3
Streamlined Plasma & Whole Blood Processing
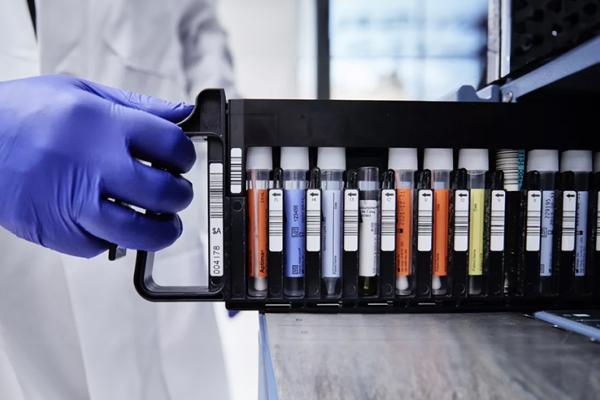
No need for aliquoting or manual sample transfer for plasma primary tube processing. Plasma tube flexibility with both PPT and EDTA tubes validated. Use pre-filled tubes for whole blood dilution, which can be loaded directly into the instrument.
Flexible Sample & Reagent Loading
No manual sample prep or barcode clips for primary tube processing. Automated barcode scanning of tubes allows positive sample identification. Run multiple assays from a single specimen tube at the same time.
Automated Analysis & Calculations
Automated QC analysis with Levey-Jennings plots to track and trend controls. Specified dilution factor for whole blood processing automatically applied.

Simplify & Scale the Future of Diagnostics
The Aptima CMV Quant Assay is part of the Hologic Molecular Scalable Solution, a portfolio combining a broad, high performing assay menu with high throughput automation. Designed to flexibly scale to meet your needs, from a single patient result to population level screening.
High Accuracy with Full Automation
The high reproducibility of the assay enhances confidence that results are accurate, regardless of where they are performed.1
40.7 IU/mL
Plasma
Limit of detection*
131.0 IU/mL
Whole blood
Limit of detection*
53 IU/mL
Plasma
LLoQ*
176 IU/mL
Whole blood
LLoQ*
1.62 to 7.3
Log IU/mL
Linear range
Demand More From Your CMV Assay¹
- Intended use: CMV viral load monitoring
- Technology: Real-time transcription-mediated amplification (TMA)
- Target region: UL56 gene
- Genotypes: 1-4
- Sample Types: Plasma and whole blood
- Sample Input Volume: Primary tube (EDTA, PPT): 1.2 mL plasma. Secondary tube: 700 μL plasma. Whole blood: 500 μL with automated dilution factor


Quantitative NAAT Testing for Rapid & Sensitive Monitoring
Human CMV is a common DNA virus that belongs to the herpes family. Its prevalence in the population ranges from 45 to 100% worldwide.4,5 Infections are typically mild or asymptomatic in people with normal immune systems. However, in immunocompromised people such as transplant recipients, CMV is a common cause of morbidity and mortality. As higher viral loads generally correlate to an increased risk of CMV disease,2,6,7,8 it is crucial that CMV levels are quantitated in transplant patients. Recent guidelines recommend at least weekly monitoring of CMV viral load post-transplant to guide decisions about starting anti-CMV therapy as well as to monitor response to therapy.
Insights
*Established using the 1st WHO International Standard
Aptima CMV Quant Dx assay [package insert]. AW-31860-001. San Diego, CA: Hologic, Inc.; 2022
Kotton CN, Kumar D, Caliendo AM, et al. The Third International Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Cytomegalovirus in Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantation. 2018;102(6):900-931.
Panther/Panther Fusion System Operator´s Manual. AW-26055-001, Rev 001, San Diego, CA: Hologic Inc.; 2022.
Bate SL, Dollard SC, Cannon MJ. Cytomegalovirus seroprevalence in the United States: the national health and nutrition examination surveys, 1988-2004. Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 1;50(11):1439-47. doi: 10.1086/652438. PMID: 20426575.
Cannon MJ, Schmid DS, Hyde TB. Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics associated with infection. Rev Med Virol. 2010 Jul;20(4):202-13. doi: 10.1002/rmv.655. PMID: 20564615.
de la Cámara R. CMV in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Mediterranean Journal of Hematology and Infectious Diseases.2016; 20;8(1):e2016031.
Emery VC, Sabin CA, Cope AV, et al. Application of Viral-Load Kinetics to Identify Patients who Develop Cytomegalovirus Disease After Transplantation. Lancet. 2000; 10;355(9220):2032.
Razonable RR, Hayden RT. Clinical Utility of Viral Load in Management of Cytomegalovirus Infection After Solid Organ Transplantation. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2013; 26(4):703-727.
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Related Products
1434
Hologic BV, Da Vincilaan 5, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium.
Notified Body number wherever applicable
EC Representative Information wherever applicable